Today, to be competitive in business, it’s very important to understand CRM reporting technology and know how to make the best out of it for a competitive edge. If you plan to check the options for your organization or are trying to distinguish various customer relationship management different tools, it helps to know how to identify true CRM reporting technology among others so that you can have informed decisions.
This all-in-one manual enables you to traverse the convoluted world of CRM reports-from inbuilt reporting capabilities to very advanced third-party solutions and enterprise-level reporting platforms. We will explore how these technologies deliver customer insights and transforms raw data into action and intelligence for business growth.
Understanding CRM Reporting Technologies

In essence, CRM reporting technology relates to all the parts of a customer relationship management system that gather and analyze data and present it in order to understand customer interactions, the sales performance of an organization, and the effectiveness of its marketing. While all the other features of CRM would, in some way, center around data entry or workflow management, the reporting technologies focus on meaningful extraction from the customer data.
"The difference between having customer data and understanding customer data is the difference between surviving and thriving in today's market," says Michael Fauscette, Chief Research Officer at G2 Crowd.
Indeed, these specific devices are not merely for viewing data but instead would provide relevance and understanding in one’s customer data. It allows you to convert what could simply be numbers into discernible insights on your customers that would be useful for informed decision making by all departments.
Industry-specific applications of CRM reporting technologies include:
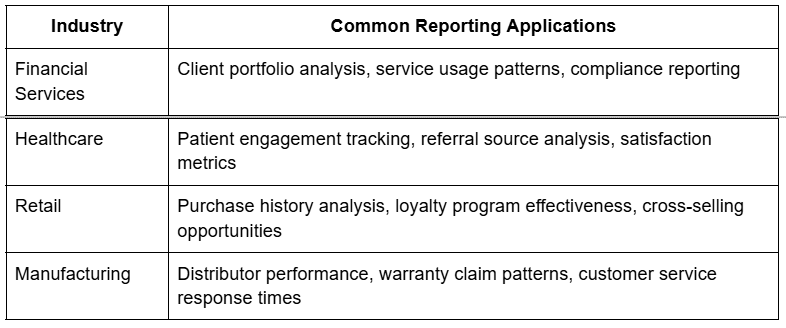
The most effective reporting technologies serve as a bridge between your customer data and your business strategy, enabling you to make data-driven decisions based on actual customer behavior rather than assumptions.
Why Effective CRM Reporting Drives Business Success
The implementation of robust CRM reporting technology directly impacts an organization’s decision-making processes and, consequently, its bottom line. Companies that effectively leverage customer insights through advanced reporting typically see improvement across multiple business metrics.
The connection between strong insightful reporting and revenue growth stems from several factors. Enhanced forecasting accuracy allows sales teams to predict future performance with greater precision when they can analyze historical patterns using sophisticated reporting tools. Faster problem identification becomes possible as well-designed reports flag potential issues before they become critical, allowing for proactive intervention.
Additionally, understanding which customers, products, or territories deliver the highest returns enables more efficient resource allocation. Perhaps most importantly, identifying at-risk customers through customer behavior analysis enables targeted retention efforts that preserve revenue.
Case Study: Transformation Through Visibility
A mid-sized insurance provider implemented advanced CRM reporting technology to address declining renewal rates. By creating dashboards that tracked customer behavior indicators of churn risk, they were able to identify at-risk policies 60 days before renewal, giving agents time to engage with customers proactively. This visibility resulted in:
- 23% reduction in policy cancellations
- 17% increase in cross-selling of additional products
- $2.4 million in preserved annual revenue
“When we could finally see the patterns in our customer data, everything changed. What was once guesswork became strategic intervention,” explained their Chief Customer Officer.
This transformation was possible because insightful reporting converted raw data into actionable intelligence that frontline staff could use to make better decisions about customer engagement.
Comparing CRM Reporting Technology Options
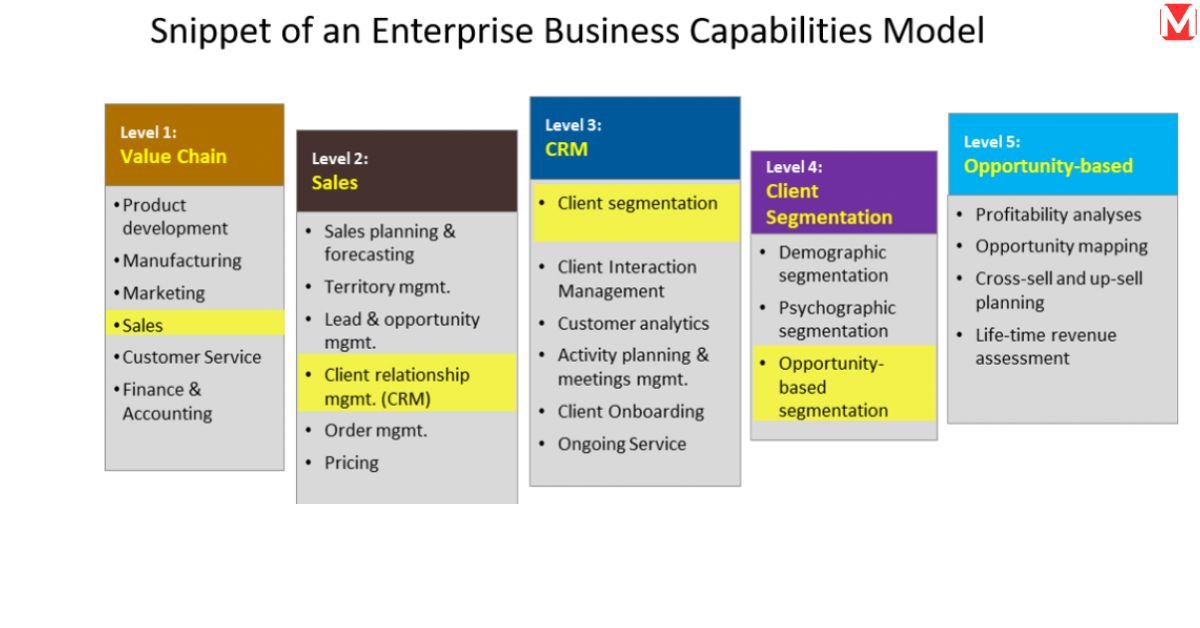
In fact, organizations usually come across three important solution types when they are considering CRM reporting technology, each with its benefits and drawbacks. Understanding these categories is imperative to being able to adopt that which will truly fit your business needs.
Native CRM Reporting Capabilities
Most CRM platforms include some form of built-in reporting as part of their core functionality. These native tools offer immediate access to basic reports without additional cost or integration requirements.
Intrinsic reporting generally, comes primarily from pre-set sales reports such as pipeline analysis and conversion rates-simple capabilities for basic customer segmentation, activity-tracking metrics, and an “out of the box” dashboard view into critical performance indicators.
For their part, Dynamics 365 reporting tools provide users with immediate access to sales forecasts, pipeline analysis, and customer engagement metrics without a requirement for supplemental software purchases. This approach fits those firms with simple reporting needs or ones that are in the beginning stages of their data analytics foray.
The internal reporting with limitations on customization, analysis depth, and the ability to blend CRM information with data from other business systems. These constraints typically emerge more in organizations’ evolution in their analytical capabilities.

Enhanced Reporting Through Third-Party Add-Ons
When native reporting capabilities prove insufficient, many organizations turn to third-party solutions that integrate with their existing CRM platform. These specialized tools offer enhanced analytical capabilities while maintaining connection to the core CRM system.
Tableau or Power BI-type analytical platforms do fall into the category of common third-party solutions, along with industry-specific reporting packages, advanced visualization systems, and custom report builders aimed at extending the functionality of the CRM.
The primary benefit of these solutions lies in enabling customers to conduct the most in-depth analysis without sacrificing investments in existing CRM systems. The third-party tools may provide more complex visualization of the data so that customers can produce interesting portrayals of it for some previously undiscoverable patterns.
Integration challenges can arise when implementing external reporting tools, however.It is quite important to plan properly in order to manage the synchronization of data with permissions for users and keep them consistent across channels. The entire ownership cost has now to be taken into consideration, which includes not only licenses and implementation services but also the maintenance part throughout.
Enterprise-Level CRM Reporting Technologies
Enterprise reporting solutions offer the widest array of support for CRM analytic functions for extremely large organizations with complex data environments. They are created to handle massive amounts of data, intricate organizational structures, and fairly sophisticated analytical requirements.
Enterprise reporting also incorporated cross systems data integration capability, advanced predictive analytics, role based dashboards and security, customizable metrics and key performance indicators (KPI), multi-channel data capture systems, to create a single view of customer interaction on ent enterprise reports.
These systems are indeed unmatched in terms of analytical capabilities; nevertheless, significant expenditures are incurred for implementation, customization, and training of users. The enterprise implementation often involves more than just the IT department; cross-functional collaboration is required and therefore will need sponsorship from top management.
Native CRM Reporting Capabilities
The foundation of CRM reporting technology often begins with the capabilities built directly into CRM platforms. These native tools provide immediate value without requiring additional software purchases or complex integrations.
Standard Reporting Functions in Major CRM Systems
Most leading CRM platforms include a core set of built-in reporting functions that address common business needs. Contact and account reports provide basic information about customer distribution, account size, and relationship duration. Sales pipeline visualization offers graphical representations of deals in progress, organized by stage, value, or sales representative. Activity metrics track calls made, emails sent, meetings scheduled, and other engagement activities. Revenue reports analyze closed business, often filterable by time period, product, or sales team.
These native capabilities handle routine reporting needs effectively, especially for smaller organizations or those with straightforward sales processes. Their primary advantages include immediate availability, consistent user experience, and direct connection to live CRM data.
In the case of Salesforce, for instance, over 50 standard report templates are provided for users to modify according to their specific needs, whereas Dynamics 365 has all kinds of reports with interactive dashboards that are updated in real-time as new data is received into the system.
Limitations of Built-in Reporting Tools
Despite their convenience, native reporting tools often fall short when organizations require more sophisticated analysis. Common limitations include restricted cross-object reporting that makes connecting data from different parts of the CRM system difficult. Limited customization constrains report layout, calculation methods, and visualization options.
As organizations grow more sophisticated in their analytical approach, these limitations often become more apparent and problematic.
When Native Reporting Makes the Most Sense
Despite these constraints, built-in reporting remains the right choice in several scenarios. Organizations just beginning their CRM journey often find native tools sufficient for their initial needs. Budget-conscious implementations where additional software purchases aren’t feasible can still derive significant value from built-in capabilities.
Companies with basic analytical needs that align with standard reporting templates can avoid the complexity of more advanced solutions. Small user bases with limited reporting users who need operational insights often find native reporting provides an excellent balance of functionality and simplicity.
Most small or medium organizations can do just fine with native reporting capabilities to give them the insight to push them toward making significant changes in their operations without the added complexity of advanced solutions.
Enhanced Reporting Through Third-Party Add-Ons
When native CRM reporting capabilities prove inadequate, organizations often seek specialized third-party solutions that can integrate with their existing CRM platform. These tools would offer enhanced analytical capability while maintaining a link to central customer data.
Popular Third-Party Reporting Solutions
The CRM-compatible reporting tools for the market have seen considerable growth with options ranging from general-purpose business intelligence platforms to highly specialized analytical tools. Well-known solutions include Tableau (fleetingly acclaimed for its data visualization capabilities and its drag-and-drop interface), Power BI (Microsoft’s business intelligence tool that works virtually seamlessly with Dynamics 365 reporting), Domo (Cloud-based platform whose major selling points are real-time data and mobile accessibility), Sisense (very strong for embedding analytics and working with large, complex datasets), and Zoho Analytics (provides great reporting features at small business prices).
But the complexity of analysis becomes additional due to information from other sources other than CRM is added as well. You can also create very beautiful representations of such analyses on these platforms by being able to analyze this data verysimply.
Integration Challenges and Solutions
Implementing third-party solutions for CRM reporting introduces several technical considerations. Data synchronization presents a significant challenge in ensuring that report data remains current. Organizations typically address this through API-based real-time connections, scheduled data syncs at appropriate intervals, or middleware solutions that manage data flow between systems.
Security and compliance considerations emerge when extending data access beyond the CRM system, requiring careful attention to permission structures and data governance. Successful implementations typically involve granular user permission mapping between systems, consistent security protocols across platforms, and audit trails for data access and manipulation.
User adoption represents another challenge, as even the most powerful reporting tools deliver value only when users actually incorporate them into decision-making processes. Effective implementations focus on intuitive user interfaces that minimize training requirements, phased rollouts that introduce capabilities gradually, and embedded analytics that integrate reporting into existing workflows.
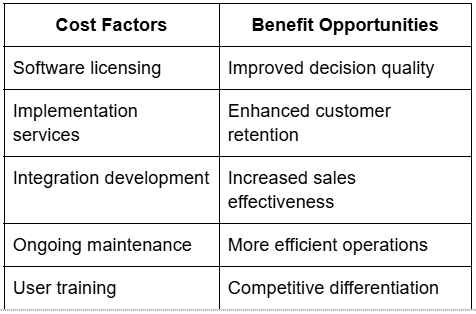
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Add-On Reporting Tools
While third-party reporting solutions require additional investment, the potential returns often justify the expense. Organizations should consider both direct costs and potential benefits:
For many organizations, the enhanced customer insights derived from third-party reporting tools translate directly to improved business outcomes. A manufacturing company that implemented a specialized analytics platform, for example, identified cross-selling opportunities that generated $1.2 million in incremental revenue during the first year—more than five times the total cost of the reporting solution.
Enterprise-Level CRM Reporting Technologies
Large organizations with complex data environments often require enterprise reporting solutions that go beyond what native CRM tools or standard third-party add-ons can provide. These sophisticated platforms offer comprehensive analytical capabilities designed to handle massive data volumes, complex organizational structures, and advanced analytical requirements.
Features that Define Enterprise Reporting
Enterprise-grade CRM reporting technology typically includes several distinctive capabilities. Cross-system data integration allows combining CRM data with information from ERP systems, marketing platforms, financial software, and other business applications. Advanced predictive modeling provides sophisticated statistical tools that identify trends and forecast future performance. Artificial intelligence components offer machine learning capabilities that detect patterns and anomalies too subtle for conventional analysis.
Customizable metrics frameworks create flexible structures that allow different business units to define and track their specific key performance indicators. Multi-tiered security models implement granular access controls that accommodate complex organizational hierarchies. Scalable architecture provides technical foundations designed to maintain performance even with massive data volumes.
These features enable large organizations to develop a unified view of customer behavior across multiple touch points, products, and business units—something impossible with simpler reporting tools.
Implementation Considerations for Large Organizations
Deploying enterprise reporting solutions involves significant complexity beyond the technical aspects of the tools themselves. Large organizations must address several critical factors. Data quality and governance becomes crucial as enterprise reporting amplifies both the value of good data and the problems caused by poor data. Successful implementations include comprehensive data cleansing and ongoing governance protocols.
Cross-functional alignment is necessary because enterprise reporting often spans departmental boundaries, requiring collaboration across traditional organizational silos. Change management becomes essential as the insights from advanced reporting frequently challenge established assumptions and business practices. Technical infrastructure may require enhancement since enterprise solutions often need significant computational resources, particularly when processing large datasets or performing complex calculations.
Organizations that address these factors methodically typically achieve more successful implementations than those focusing exclusively on technical aspects.
Scalability and Performance Factors
As data volumes grow and analytical requirements evolve, the ability of reporting technologies to maintain performance becomes increasingly important. Enterprise solutions must balance several competing priorities including processing efficiency to optimize query performance even with massive datasets, user responsiveness to maintain acceptable response times during peak usage periods, resource utilization to balance computational demands with available infrastructure, and growth accommodation to adapt to increasing data volumes without requiring architectural redesign.
Leading enterprise reporting platforms address these challenges through various technical approaches, including in-memory processing, distributed computing architectures, and intelligent caching mechanisms. When evaluating enterprise solutions, organizations should consider both current requirements and projected growth in data volume and complexity.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Reporting Capabilities
Microsoft’s Dynamics 365 platform offers a comprehensive suite of reporting technologies that combine native capabilities with deep integration to Microsoft’s broader business intelligence ecosystem. This hybrid approach provides organizations with significant flexibility in how they approach CRM analytics.
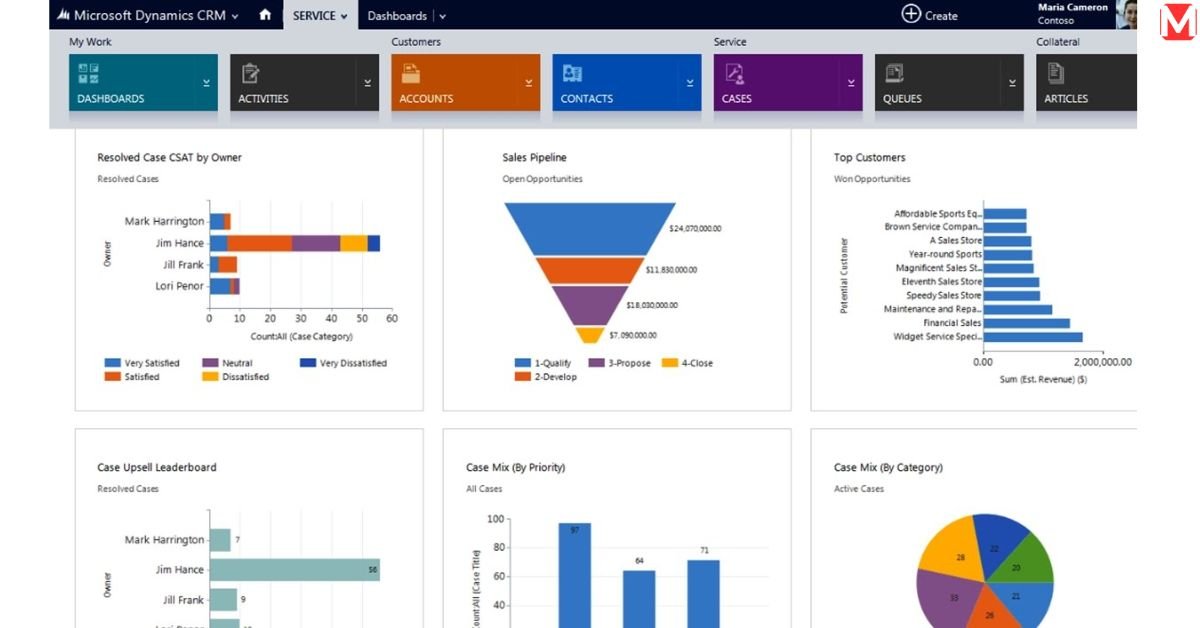
Built-in Reporting Functionality Overview
Dynamics 365 reporting begins with a robust set of native capabilities including interactive dashboards (customizable visual interfaces that present key metrics in real-time), standard reports (pre-built reports addressing common business requirements), advanced filters (sophisticated criteria for segmenting and analyzing data), export capabilities (options for sharing reports in multiple formats), and role-based views (tailored perspectives that align with different user responsibilities).
These core features provide immediate value without requiring additional software or complex configuration. Many organizations find that these built-in capabilities address a significant portion of their reporting needs, particularly for operational metrics and day-to-day decision support.
“Dynamics 365 reporting gave us immediate visibility into our pipeline that we simply didn’t have before,” explains the Sales Operations Director at a mid-sized manufacturing firm. “The ability to customize dashboards for different roles means our sales managers see the metrics most relevant to their teams.”
Power BI Integration Advantages
The true strength of Dynamics 365 reporting emerges when organizations leverage its seamless integration with Power BI, Microsoft’s business intelligence platform. This combination delivers several distinct advantages including enhanced visualization (access to Power BI’s extensive library of visualization options), cross-system analysis (ability to combine CRM data with information from other business systems), advanced analytics (utilization of statistical functions, predictive models, and AI-driven insights), self-service capabilities (tools that allow business users to create their own reports without IT assistance), and embedded analytics (options for incorporating analytics directly into operational applications).
This integration allows organizations to start with simple reporting and gradually expand their analytical capabilities as needs evolve and users become more sophisticated in their approach to data.
Real Implementation Examples
Organizations across industries have leveraged Dynamics 365 reporting to transform their approach to customer data. Consider these examples:
Financial services: A regional bank implemented custom Power BI dashboards that combine Dynamics 365 customer data with transaction information from their core banking system. This integrated view helps relationship managers identify cross-selling opportunities based on actual customer behavior, resulting in a 14% increase in products per customer.
Healthcare: A medical device manufacturer uses Dynamics 365 reporting to analyze the relationship between sales rep activities and eventual purchasing decisions. Their analysis revealed that facilities receiving quarterly in-service training were 37% more likely to purchase premium products, leading to a restructuring of their customer engagement model.
Professional services: A consulting firm developed Power BI scorecards that track client engagement health by monitoring multiple indicators from Dynamics 365, including response times, issue resolution rates, and sentiment analysis from client communications. This early warning system has improved their client retention rate by 23%.
These examples illustrate how organizations can leverage the flexibility of Dynamics 365 reporting to address their specific business challenges while maintaining a unified view of customer relationships.
Tableau as a CRM Reporting Solution
While many organizations leverage CRM-specific reporting tools, others choose general-purpose data visualization platforms like Tableau to analyze their customer data. This approach offers distinctive advantages for certain types of analysis and organizational contexts.
Tableau's Unique Advantages for CRM Data
Tableau has established itself as a leader in data visualization with several characteristics that make it particularly valuable for CRM analytics. Its exceptional visual capabilities go beyond standard charts to include sophisticated options like heat maps, tree maps, bubble charts, and geographic visualizations. An intuitive interface with drag-and-drop functionality allows business users to explore data without requiring technical expertise.
Powerful data blending provides advanced capabilities for combining information from multiple sources. A strong mobile experience offers fully-featured mobile apps that maintain visual impact on smaller screens. Access to a broad user community provides extensive resources, templates, and shared knowledge across industries.
These features make Tableau particularly effective for exploratory analysis of customer behavior and complex pattern recognition that might not be apparent in standard tabular reports.
Integration Methods with Popular CRM Systems
Organizations typically connect Tableau to their CRM systems through one of several methods. Direct database connections link Tableau directly to the underlying CRM database. API integration uses the CRM system’s application programming interfaces to access data. The data warehouse approach extracts CRM data to a central repository that also contains information from other systems. Pre-built connectors utilize specialized connection tools developed for specific CRM platforms.
Each approach offers different trade-offs in terms of implementation complexity, refresh frequency, and ability to combine CRM data with other information sources. Organizations should select the integration method that best aligns with their technical environment and analytical requirements.
Visual Analytics Capabilities for Customer Insights
Tableau’s strength in visual analysis allows organizations to derive distinctive customer insights that might remain hidden in traditional reports. Relationship mapping visualizes connections between customers, products, and interactions. Behavioral clustering identifies groups of customers with similar patterns of engagement. Geographical analysis examines customer distribution, regional performance, and territory management. Temporal patterns recognize seasonal trends, lifecycle patterns, and activity correlations. Multivariate comparison analyzes the relationship between multiple variables simultaneously.
A retail organization used Tableau to analyze the relationship between customer purchase frequency, average order value, and product category preferences. The resulting visualization revealed distinct customer segments that responded differently to promotional offers, allowing the marketing team to develop more targeted campaigns that improved response rates by 34%.
Measuring ROI from CRM Reporting Technologies
Implementing CRM reporting technology requires investment in software, services, and organizational change. Measuring the return on this investment helps organizations validate their decisions and guide future enhancements to their analytical capabilities.
Key Performance Indicators to Track
Effective measurement of reporting ROI focuses on both the direct impact of the technology and the business outcomes it enables:
- Technology-specific metrics: Report usage rates (by user, department, report type), time spent accessing and analyzing information, user satisfaction with reporting tools, data quality improvements, and report creation efficiency
- Business outcome metrics: Conversion rate improvements, customer retention increases, revenue growth from existing customers, sales cycle acceleration, marketing campaign effectiveness, and customer service efficiency
Organizations should establish baseline measurements before implementing new reporting technologies and track changes as users adopt the new capabilities. The most compelling ROI calculations combine quantitative metrics with qualitative assessment of how improved information access affects decision quality.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I identify true CRM reporting technologies?
True CRM reporting technology goes beyond simple data presentation to provide meaningful analysis of customer relationships. Look for capabilities that connect data points across the customer journey, provide context for metrics through benchmarking or historical comparison, enable segmentation based on meaningful customer characteristics, allow exploration of relationships between different variables, and support both tactical decisions and strategic planning.
What are implementation best practices for CRM reporting?
Successful implementation of reporting technologies typically follows several key principles. Starting with clear business objectives rather than technical features establishes the right foundation. Involving end users in requirements definition and design increases adoption rates. Implementing in phases, beginning with high-value, relatively simple reports builds momentum and credibility. Providing adequate training tailored to different user roles ensures effective utilization. Establishing data governance protocols ensures report accuracy and trustworthiness. Creating feedback mechanisms enables continual refinement of reporting capabilities.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right CRM Reporting Technology
Choosing the appropriate CRM reporting technology represents a critical decision that affects an organization’s ability to derive value from its customer data. The ideal solution balances technical capabilities with organizational needs and supports both current requirements and future growth.


