What is QaaS Technology? Your Ultimate Guide

Ever heard of quantum computing and thought it sounded like a futuristic fantasy? Well, what is QaaS technology if not the key to making that fantasy real today? Short for Quantum as a Service, QaaS brings jaw-dropping computational power to your laptop via the cloud. No need for a billion-dollar lab just a subscription.
In 2024, IBM’s quantum network hit 250,000 users, showing this is not some niche experiment anymore. Curious? Let’s explore what QaaS technology is and why it’s shaking things up.
Why QaaS Matters Right Now
Imagine a logistics company cutting delivery times by 30% with a few clicks. That’s the magic of what is QaaS technology in action. It’s not just for scientists—businesses, coders, and innovators are jumping in. Cloud quantum computing through QaaS makes cutting-edge tech accessible to you, no PhD required.
Amazon Braket, for instance, saw a 50% usage spike in 2024 as companies tapped into quantum computing resources. So, what is QaaS technology really about? Stick with me it is worth knowing.
Defining QaaS: Quantum Power in Your Hands

So, what is QaaS technology at its core? It’s a cloud-based service that delivers quantum computing solutions over the internet. Forget owning a quantum computer—QaaS lets you rent its power. Classical computers use bits: 0 or 1. Quantum systems use qubits, which can be 0, 1, or both at once due to superposition. Toss in entanglement—where qubits link up in spooky ways and you’ve got a beast that solves problems differently.
Think of it like renting a streaming service, but instead of movies, you get quantum platforms. Big players host the quantum computing infrastructure, and you tap in. It’s affordable access to a tech once locked in elite research labs. That’s the heart of what QaaS technology offers power without the price tag.
How QaaS Works: The Nuts and Bolts

Curious about what is QaaS technology behind the scenes? Here’s the rundown. You connect to a cloud platform with quantum hardware—like superconducting qubits or trapped ions. Tools like IBM’s Qiskit or Google’s Cirq let you write quantum algorithms and experiments. Send your code over the internet, and it runs on real quantum processors or simulators. Results pop back fast—sometimes in minutes.
Many setups use hybrid quantum computing, mixing quantum and classical systems. Why? Quantum excels at specific tasks—like optimization—but leans on classical tech for the rest. Picture renting a jetpack for a quick flight, but keeping your car for the commute. With cloud-based quantum access, you scale usage as needed, no huge investment upfront. That’s the practical side of what QaaS technology delivers.
Standout Features of QaaS: What Sets It Apart
What is QaaS technology without its cool perks? Check out these standout features:
- Remote Access: Run quantum tests from anywhere—your couch, a café, you name it.
- Hardware Options: Choose from photonic setups, ion traps, or annealing systems—variety rules.
- Simulation Tools: Play with quantum simulations before hitting real hardware.
- Integration: APIs and SDKs tie QaaS into your workflows effortlessly.
Whether you are coding quantum programming for fun or solving big problems, QaaS fits. D-Wave’s Leap targets optimization with annealing, while IBM offers versatile quantum circuits. That’s what makes QaaS technology a standout.
Real Benefits of QaaS: Why You’d Want It

So, what is QaaS technology good for? Plenty. It’s cost-effective—building a quantum lab runs $10 million plus, but QaaS starts at a few hundred bucks monthly. Speed’s another win. Quantum computing applications like molecular modeling finish in hours what classical systems drag out for years.
It sparks innovation too. Experiment fast, fail cheap, and score breakthroughs. A German shipping firm used quantum cloud services via D-Wave to cut route-planning time by 25% in 2023. Plus, it scales. As quantum computing providers upgrade hardware, your access improves without extra cost. That’s the why behind what QaaS technology brings to the table.
QaaS in Action: Killer Applications Across Industries
What is QaaS technology doing out there? Transforming industries—here’s how:
- Cryptography: Quantum security protocols like post-quantum cryptography keep data safe. NIST rolled out quantum-safe standards in 2024.
- Drug Discovery: Simulate molecules quick. Merck used IBM’s QaaS for protein folding, speeding drug R&D.
- Finance: Quantum financial modeling optimizes portfolios. JPMorgan Chase boosted precision 15% with Azure Quantum in 2023.
- Logistics: Solve complex routes. Volkswagen’s quantum trials with D-Wave cut urban delivery times by 20%.
Case Study: BMW teamed up with Amazon Braket in 2022 to optimize factory layouts. Using quantum-assisted computing, they tested thousands of setups in a day impossible with classical tech. From AI to materials, quantum-powered innovation via QaaS is real.
Who’s Leading the QaaS Pack: Top Players to Know
What is QaaS technology without its pioneers? Meet the top quantum computing providers:
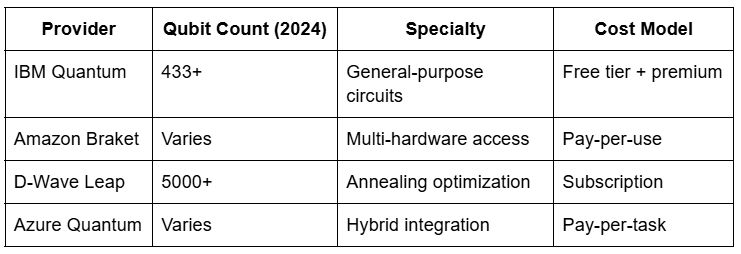
- IBM Quantum: Qiskit-powered, with a 433-qubit Osprey chip (2022). Targets 1000+ qubits by 2026.
- Amazon Braket: Multi-hardware access—Rigetti, IonQ, D-Wave. Usage jumped 50% in 2024.
- Microsoft Azure Quantum: Strong on hybrid computing models with Q# language.
- D-Wave Leap: 5000-qubit Advantage system (2020) for optimization fans.
- Google Quantum AI: 72-qubit Bristlecone chip, mostly for research partners.
Emerging names like QuEra (256-qubit neutral atoms) and Xanadu (photonic quantum) add flair. IBM scales wide, D-Wave digs deep—variety defines what QaaS technology offers.
QaaS’s Promise and Pitfalls
What is QaaS technology headed for? The future of quantum computing looks exciting but not smooth. Qubit counts are rising IBM eyes 1000 by 2026 and error correction’s getting better. Adoption’s up too. Gartner forecasts 20% of Fortune 500 firms testing quantum cloud platforms by 2027. Costs are falling, widening access.
Challenges persist, though. Noisy qubits mess up big calculations. Skills are scarce only 1 in 5 developers grasp quantum basics, per a 2024 survey. Security’s a wild card quantum encryption could crack today’s codes, pushing quantum-safe algorithms. Still, quantum computing trends hint at real wins by 2030. As IBM’s Dario Gil says, “Quantum amplifies classical it doesn’t replace it.”
Getting Started with QaaS: Your Next Move
What is QaaS technology if you can’t try it? Here’s your starter kit:
- Choose a Platform: IBM’s free tier (5 qubits) or Braket’s trial work great.
- Learn Basics: Hit Qiskit.org or Microsoft’s Quantum Learning for quantum code execution tips.
- Start Small: Test a simple algorithm—like a random number generator—on a simulator.
No rocket science here just curiosity. A friend in logistics cracked a warehouse puzzle with D-Wave’s Leap in a weekend. Resources like Qiskit’s docs (qiskit.org) or Braket’s guides (aws.amazon.com/braket) get you going. That’s what QaaS technology hands you—access, simplified.
Wrapping It Up: QaaS as Your Quantum Key
So, what is QaaS technology in the end? It’s your gateway to quantum power affordable, potent, and ready now. From quantum research and development to quantum-enhanced applications, it’s rewriting the playbook. Logistics, finance, security you name it, QaaS touches it. The future’s quantum don’t lag in the classical past.






