Inside Apple’s $100 Billion US Manufacturing Boost: What Trump’s Announcement Means for American Jobs and Tech in 2025
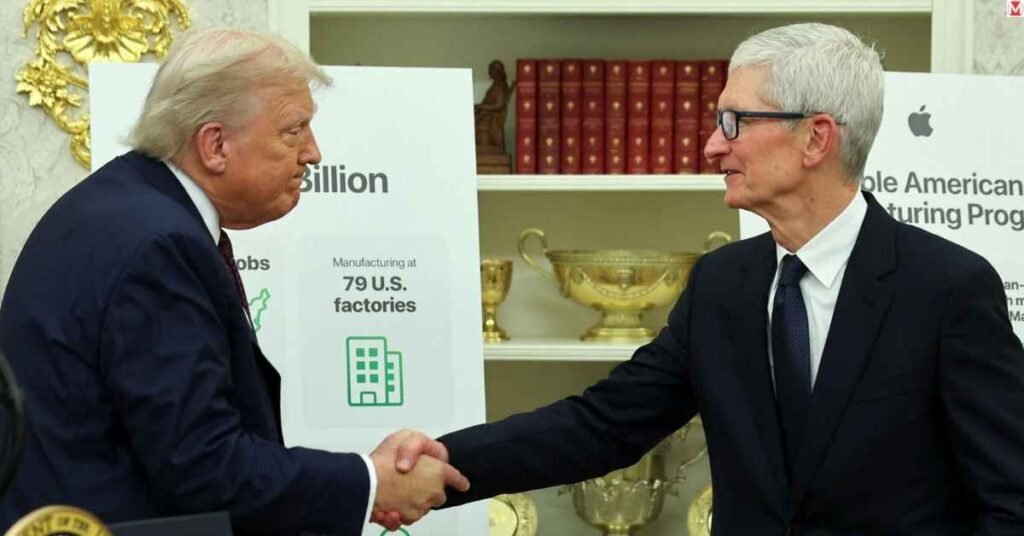
Apple’s $100 Billion US Manufacturing Boost just became reality with Wednesday’s announcement alongside President Donald Trump. This massive Apple US investment represents more than just corporate spending. It’s reshaping how America builds technology and creates jobs in the digital age. The new $100 billion investment spans four years, bringing Apple’s total domestic commitment to an impressive $600 billion. This Apple manufacturing expansion signals the biggest shift in tech production since companies moved operations overseas decades ago. Apple’s $100 Billion Shock: What It Means This isn’t your typical corporate announcement. Apple’s $100 billion US Manufacturing Boost comes at a critical moment when Trump threatened to levy large import taxes on chips entering the country. The timing tells you everything about Apple’s strategy. Apple seeks to avoid punishing tariffs on its flagship iPhones while securing its position as America’s favorite tech company. The numbers are staggering – this Apple US economic boost equals roughly 15% of Apple’s current market value. READ ALSO: Exploring the Game-Changing Features of iOS 26 and Android 16: What Smartphone Users Will Experience in 2025 Here’s what makes this Apple manufacturing investment plan different: $600 billion total commitment over four years 20,000 direct jobs planned across multiple states $2.5 billion glass factory specifically for iPhone production Advanced chip manufacturing through TSMC partnership The Apple 2025 US expansion builds on mass production of 4-nanometer chips that began late last year. These aren’t tomorrow’s promises – they’re today’s reality. Why Apple Is Doubling Down on U.S. Manufacturing Tim Cook’s decision reflects harsh political realities. The Trump Apple announcement 2025 comes after years of trade tensions and tariff threats. Trump’s administration previously threatened 25% tariffs if Apple failed to move iPhone manufacturing to the United States. Why an Apple reshoring initiative also adds up. COVID-19 and trade wars forced Apple to spend the past year-and-change learning those lessons, about both how interconnected global supply chains are The company now considers it prudent to invest in domestic production as a hedge against future emergencies. The key to Apple’s domestic manufacturing strategy is being able to make the most important components here first. TSMC’s Phoenix Fab To Employ 6,000 High-Tech, High-Wage Jobs Plus Provide Support For Another 10,000 Jobs In The Area | SemiWiki And this ripple effect, of course, multiplies throughout local economies. As Plagmatic further explains, the Apple supply chain USA transformation also eliminates or lessens geopolitical risks. The chip manufacturing is on-shore in the US, reducing further risk related to Taiwan/China tensions around Apple’s precious goods. Jobs, Plants, and Supply Chains: The Real Impact Apple’s $100 billion US Manufacturing Effort Represents Actual Employment Opportunities for Americans There are 2,000 workers making chips in the US for TSMC now, but we’re just getting started. The Apple US jobs creation breaks down into several categories: Direct manufacturing positions at chip fabs and assembly plants Engineering roles for process development and quality control Support services from security to food service Construction jobs building new facilities READ ALSO: How I Turned NotebookLM Into My Personal AI Study Assistant to Master Complex Subjects Without Stress TSMC’s Arizona commitment creates 6,000 permanent and 20,000 temporary jobs. These aren’t minimum-wage positions either. Semiconductor manufacturing requires skilled technicians earning $60,000-$120,000 annually. The Apple factory locations US strategy spreads benefits nationwide. Arizona gets the massive TSMC facility. The $2.5 billion iPhone glass factory will likely partner with Corning, which already operates facilities in New York and Kentucky. Apple manufacturing plants in USA represent a complete ecosystem shift. Instead of shipping components across oceans, Apple builds integrated supply networks. This Apple infrastructure investment reduces costs, delivery times, and environmental impact. Tariffs, Trade, and the Politics Behind the Deal The Trump-Cook relationship evolved from hostile to collaborative. Early in Trump’s first term, he threatened massive tariffs on Apple products. Now they’re announcing the largest Apple corporate investment USA has ever seen. Apple’s $100 Billion US Manufacturing Boost serves both parties’ interests. Trump gets to claim victory on bringing manufacturing home. Apple gets protection from potentially devastating import taxes on its most profitable products. The Apple tariffs manufacturing deal creates a template for other tech companies. Google, Microsoft, and Meta face similar pressures to increase domestic production. Apple’s move forces competitors to follow or risk being labeled as less patriotic. This Apple and US trade policies alignment affects global markets too. China loses some Apple production, though the company maintains significant operations there. The Apple boost to American economy comes partly at China’s expense. Investment Component Amount Timeline Previous Commitment $500 billion 2021-2025 New Investment $100 billion 2025-2029 Glass Factory $100 billion 2025-2029 Glass Factory $2.5 billion 2025-2027 Total Commitment $600 billion 4 years Where Apple Will Build — State-by-State Wins Arizona emerges as America’s semiconductor capital through this partnership. TSMC’s investment represents the largest foreign direct investment in Arizona’s history. The state now hosts some of the world’s most advanced chip production. Apple chip production Arizona utilizes cutting-edge technology. TSMC makes 90% of the world’s most advanced chips, and their Phoenix facility brings that expertise to American soil. READ ALSO: How I Customized the Samsung Galaxy Tab S10 Ultra’s Hidden Developer Gesture Controls to Streamline My Workflow in 2025 Other states benefit from Apple’s supply chain expansion: New York: Corning Glass Manufacturing Partnerships Kentucky: Existing Apple manufacturing presence expansion California: Design and engineering centers Texas: Potential future facility locations The Apple state-by-state investment breakdown was a strategic cut-and-dry move. Apple selects sites in part for their proven history of tech support, proximity to skilled workers, and a welcoming business climate. Manufacturing partnerships for Apple production in Kentucky already support thousands of jobs. In addition to extending the important relationships we have with our customers and partners, it also unlocks new, dramatic opportunities in adjacent semiconductor markets. READ MORE ABOUT: Trump announces Apple investing another $100 billion in US manufacturing Can This Move Keep iPhones ‘Made in America’? There are substantial obstacles ahead for the Made in America Apple products dream. The iPhone is made up of around 200 individual parts